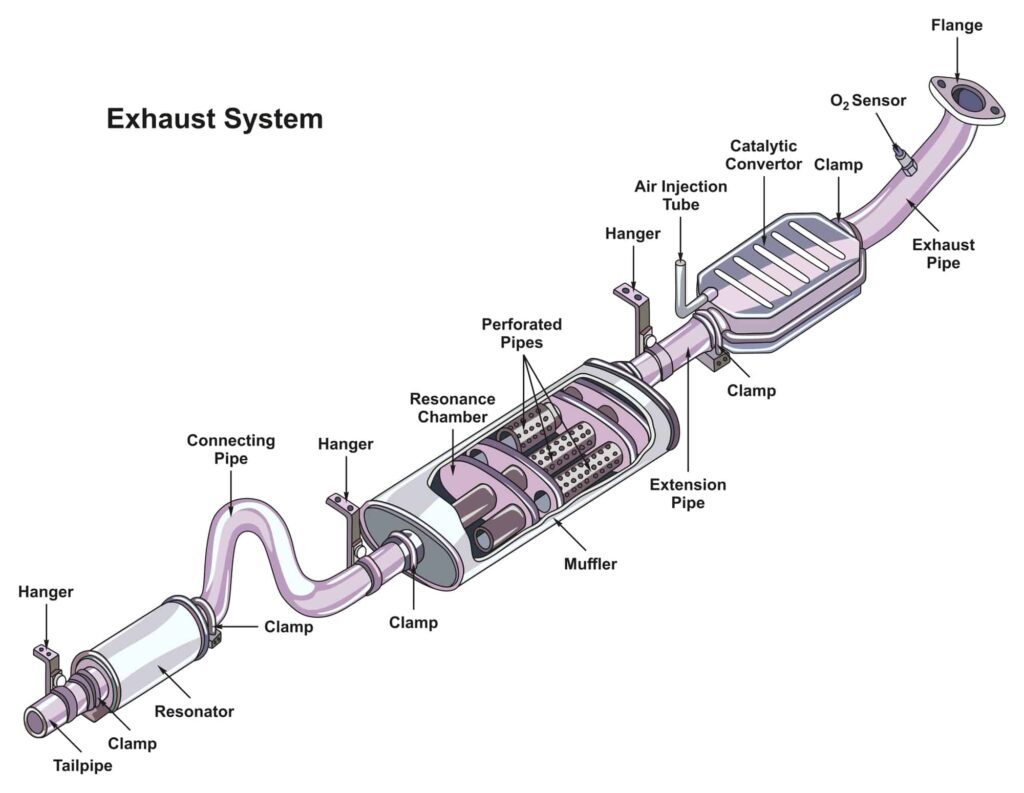
Your vehicle’s exhaust system has a hardworking component that often goes unnoticed—the catalytic converter. While it may not get the attention your engine or brakes do, this hidden hero plays a critical role in reducing harmful emissions and keeping your car running smoothly. However, when it begins to fail, the consequences can quickly become apparent.
In this article, we’ll explore why your catalytic converter matters, the most common catalytic converter failure symptoms, and the top causes behind its breakdown.
What Makes the Catalytic Converter the Hidden Hero?
The catalytic converter is a vital part of your vehicle’s exhaust system, working quietly to transform harmful pollutants—like carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides—into less harmful emissions before they exit your tailpipe. This process keeps your vehicle environmentally friendly and compliant with emissions standards.
But its role goes beyond just protecting the environment. A properly functioning catalytic converter also supports optimal engine performance. When it fails, drivers often experience clear catalytic converter failure symptoms, such as reduced engine power, unusual smells (often described as rotten eggs), and an illuminated check engine light.
Catalytic Converter Clogged? Here’s What Can Happen
When the catalytic converter becomes clogged, it can’t efficiently process exhaust gases. This leads to a number of problems, including:
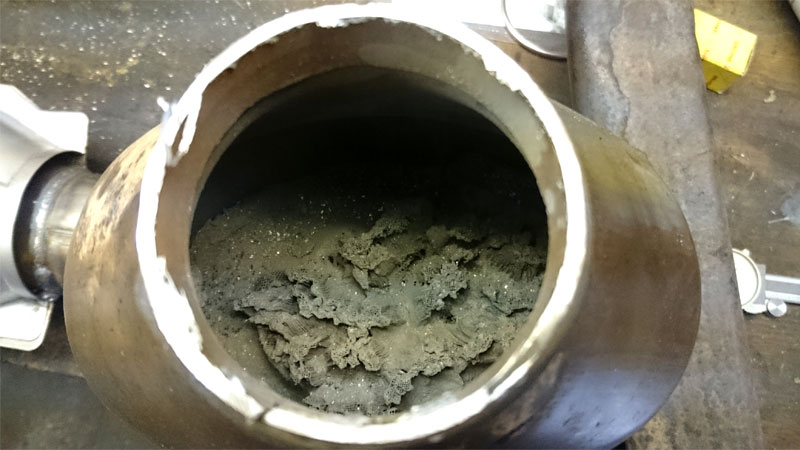

- Reduced Engine Power: A clogged catalytic converter restricts exhaust flow, causing sluggish acceleration and poor fuel efficiency.
- Overheating Risks: Blockages in the exhaust system can lead to heat buildup, damaging engine components and increasing the risk of engine failure.
- Failed Emissions Tests: A failing catalytic converter can’t effectively reduce emissions, often leading to a failed smog check.
These catalytic converter failure symptoms are early warning signs that your exhaust system needs immediate attention.

Top 3 Causes of Catalytic Converter Failure
- Engine Misfires
Engine misfires send unburned fuel into the exhaust system. This unburned fuel overheats the catalytic converter, damaging the internal catalyst material and leading to failure. - Oil or Coolant Contamination
Oil or coolant leaks into the combustion chamber can coat the catalyst inside the converter. This contamination leads to clogging and reduces the converter’s ability to process exhaust gases effectively. - Age and Mileage
Most catalytic converters are designed to last between 100,000 and 150,000 miles. Over time, the catalyst materials degrade, diminishing efficiency and leading to catalytic converter failure symptoms.
How to Prevent Catalytic Converter Trouble
Routine vehicle maintenance is key to preventing catalytic converter failure symptoms. Address engine misfires quickly, fix coolant or oil leaks, and keep up with regular oil changes. These simple steps can help extend the life of your catalytic converter.
If you notice a decrease in engine power, poor fuel economy, or a sulfur-like odor, don’t ignore these catalytic converter failure symptoms. At Douglas Automotive, we specialize in diagnosing and repairing exhaust system issues, including catalytic converter problems.
Contact us today to schedule a diagnostic service and ensure your vehicle continues to run clean, efficient, and reliable.


